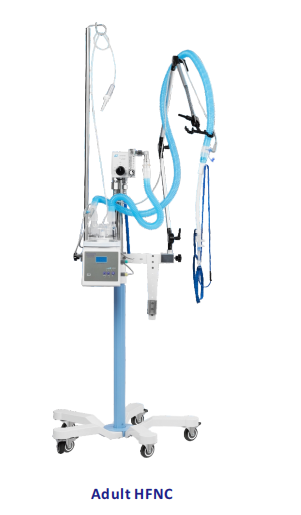
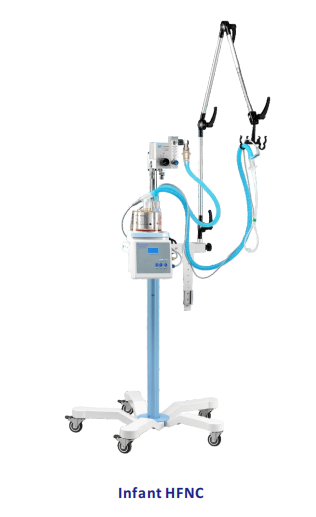
HFNC (High Flow Nasal Cannula)
tComposition
?Air-oxygen mixer
?Heated humidified water tank
?Breathing tube (built-in heating circuit)
?Nasal congestion connected to the patient
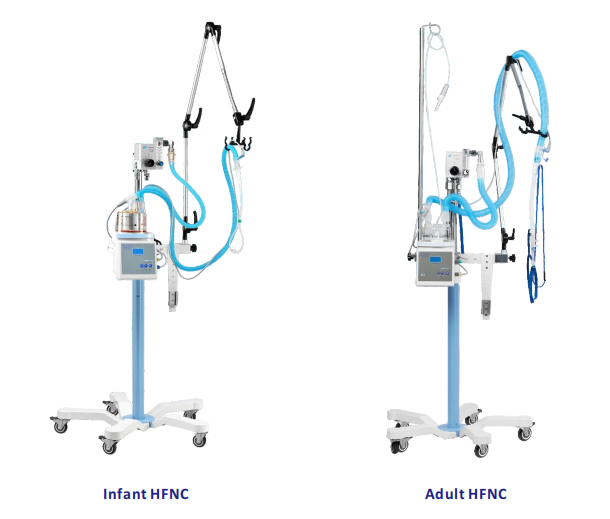
tTechnical Parameter
| Model | Infant HFNC | Adult HFNC |
| Flow | 2 - 18 LPM | 6 - 60 LPM |
| FiO2 | 21%-100% | 21%-100% |
| Accuraty of FiO2 | ± 3% | ± 3% |
| Gas source | Oxygen & Air @ 0.3-0.4 MPa | Oxygen & Air @ 0.3-0.4 MPa |
| Output gas temperature (PN2000-FB) | Heater wire mode: 25 - 40℃ | Heater wire mode: 25 - 40℃ |
| Humidifcation chamber | Reusable | Auto-fill and disposable |
| High-flow nasal cannula | Large, Medium, Small | Large, Medium, Small |
| Optional Air-compressor | PN-4000 | PN-3000 |
| Alternative Humidifier | PN-2000FC850 / PN-2000FB | PN-2000FC850 / PN-2000FB |
tOptional
Optional medical air compressor
tClinically Indicated
1. After the high-flow gas enters the pharynx through the nose, a fresh gas storage room will be created due to the scouring effect, which can reduce carbon dioxide and then inhale;
2. The high-flow gas is close to the patient's peak inspiratory flow, and it is no longer necessary to inhale some additional air from the air as a supplement, so the patient's actual inhaled oxygen concentration (FiO2) is more reliable;
3. High-flow gas delivery can reduce the patient's inspiratory work and provide low-level respiratory support;
4. High-flow gas can generate low-level positive airway pressure, thereby increasing the average tunnel pressure throughout the breathing cycle.